Summary:
- What are the seven Australian Professional Standards for Teachers?
- What are the three domains?
- Why do we have the APST?
- How do I know what level of the APST I am working at?
The Australian Professional Standards for Teachers are a set of standards that Australia expects every teacher to meet across the country. The seven standards outline all of the things teachers in Australia are expected to do, as well as how well they are expected to do them at different career stages. The standards are outlined by the Australian Institute for Teaching and School Leadership (AITSL).
See more: Australian Professional Standards for Teachers Terminology Explained
What are the seven Australian Professional Standards for Teachers?
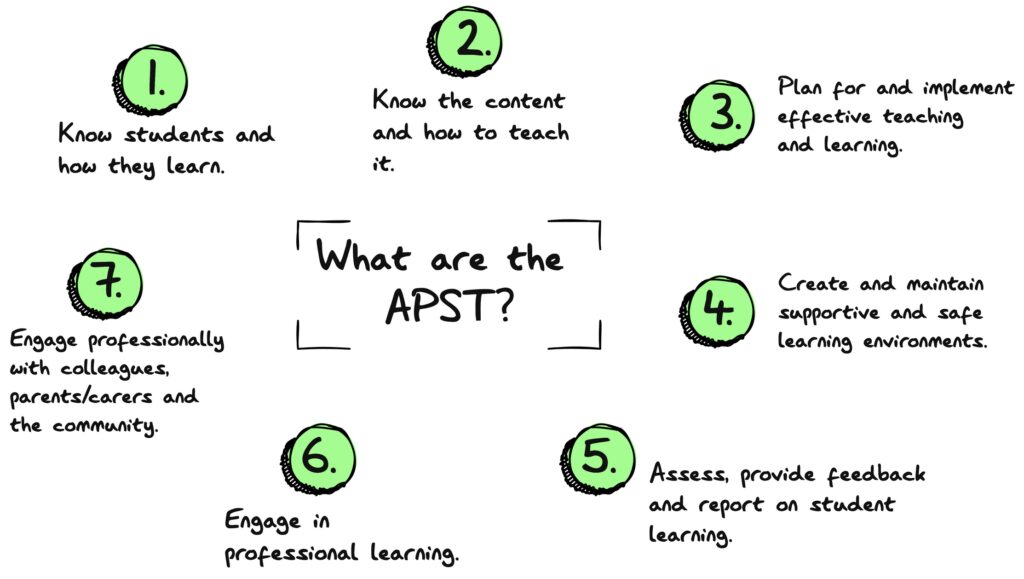
The seven APST are:
- Know students and how they learn.
- Know the content and how to teach it.
- Plan for and implement effective teaching and learning.
- Create and maintain supportive and safe learning environments.
- Assess, provide feedback and report on student learning.
- Engage in professional learning.
- Engage professionally with colleagues, parents/carers and the community.
Each of these standards are further broken down into descriptors which give specific details about what is expected in each standard and how teachers can make sure they are meeting them. While these standards remain the same for all teachers at all career stages, the descriptors change as a teacher moves up each level.
What are the three domains of the Australian Teacher Standards?
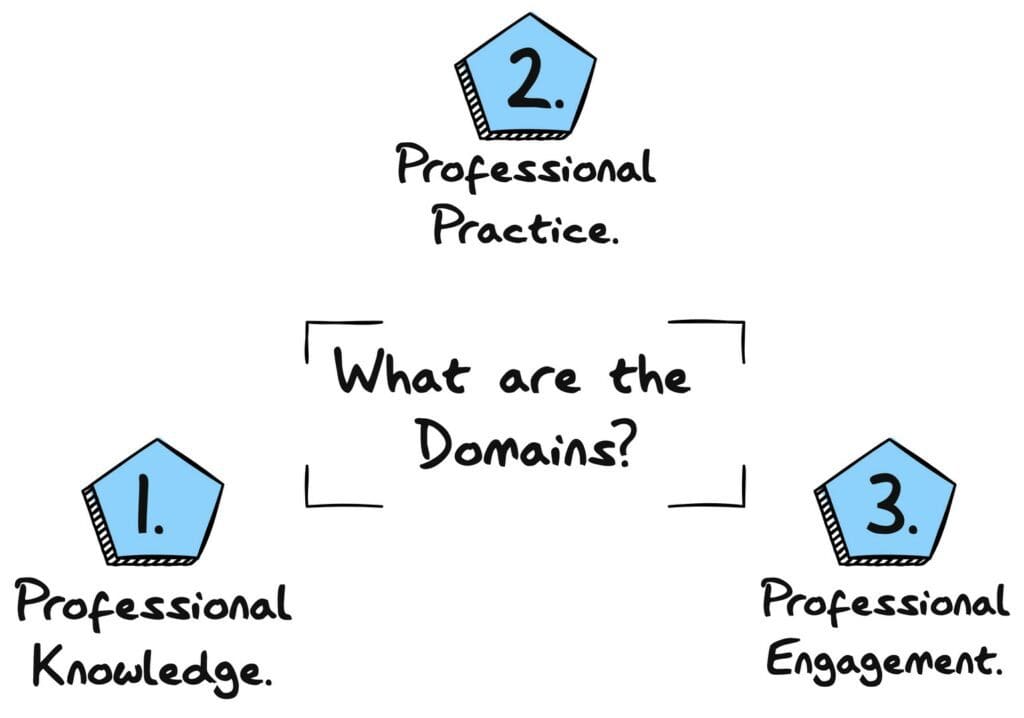
The seven APST are split into three domains:
These three domains are an important way of simplifying and explaining the role of teachers in Australia, although they are not directly used for accreditation like the individual standards are.
Professional Knowledge
The Professional Knowledge domain contains two standards:
This domain is all about what professional knowledge you have about teaching and learning. This includes how well you know the content that you are teaching (such as English or Mathematics), but also how well you understand the theory behind teaching young people. This knowledge forms the foundation that you need for the other domains.
Your understanding of your students is a key part of being a teacher and is outlined in this domain. As a teacher, you need to know how the minds of young people work in general, as well as how to teach your students specifically. Because of this, this domain is very broad and can reach from understanding constructivism and the basic structure of the brain, to understanding how to support your students with ADHD or trauma.
Professional Practice
The Professional Practice domain contains three of the Australian Professional Standards for Teachers:
- Plan for and implement effective teaching and learning.
- Create and maintain supportive and safe learning environments.
- Assess, provide feedback and report on student learning.
This group of standards make up most of the day-to-day work of teachers. Moving through each of these three standards, they cover the planning of learning, the work done with students in class, and giving marking and feedback after students have demonstrated their learning.
The standards in this domain are very much things that teachers do with their students. If you want to move up to the next career stage as a teacher, these are the things that you often need to demonstrate and provide evidence for. Often, this evidence will come in the form of lesson observations as these provide the best evidence of a teacher’s professional practice.
Professional Engagement
The Professional Engagement domain contains the final two standards:
- Engage in professional learning.
- Engage professionally with colleagues, parents/carers and the community.
This domain outlines what teachers need to do outside of the classroom to build their skills and knowledge as well as build relationships and connections with their communities. Teachers need to make sure that they are connected to current research and best practice as well as to their colleagues and stakeholders to make sure that they are doing the best job that they can for their students. The standards in this domain outline what is expected of teachers in this regard.
See more: How to Present a Great Professional Learning Workshop
Why do we have the APST?
The APST are a way for schools and tertiary institutions to have a common understanding and language around what the role of a teacher actually is. Universities use these standards to build their programs so that they know that their graduates will be meeting the standard set by schools and registering bodies across the nation. Many of these registering bodies around Australia use these standards to ensure the quality of the teachers who they register, regardless of where they studied.
These common standards also make it easier for teachers to move between states and make sure that schools (as well as the teachers themselves) understand and what is expected of a teacher in Australia.
How do I know what level of the APST I am working at?
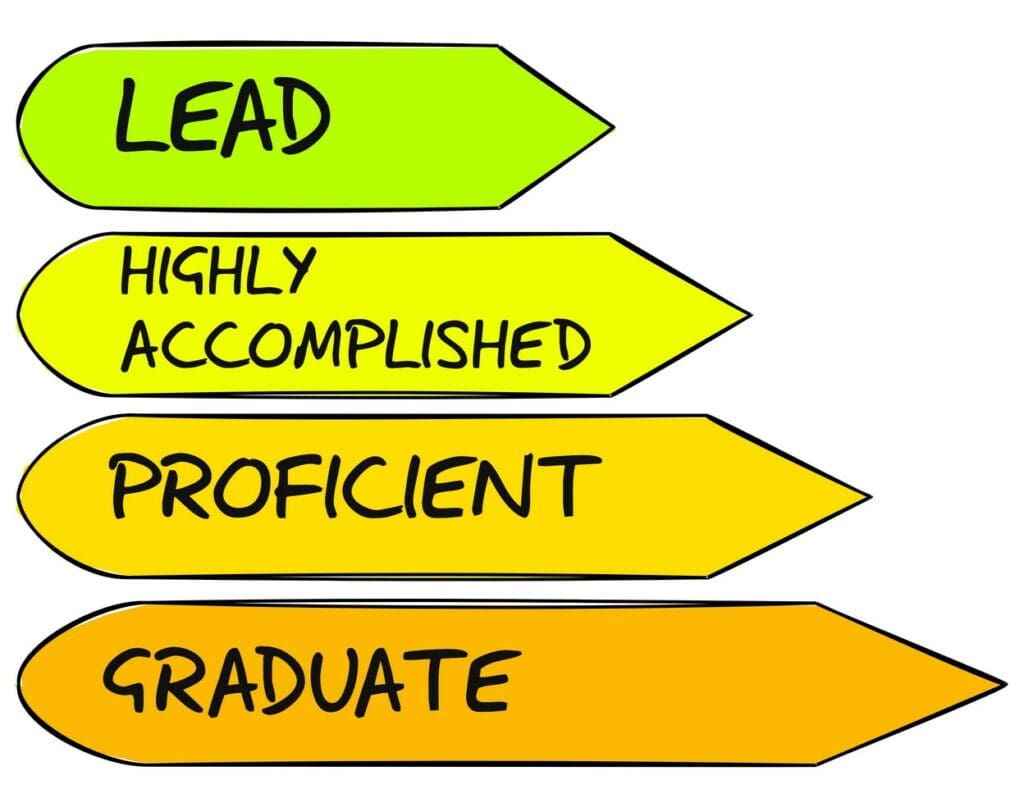
If you want to better understand how good of a teacher you are, you can have a look at the descriptors for each of the seven standards. The four levels of the APST are:
Each of the seven standards will have different descriptors for each of these levels which outline exactly what teaching practice looks like at each level. If you want to know which level you are working at, you will need to look at the descriptors for each of the standards and see which ones suit your practice best.
University programs in Australia need to ensure that you’ve met the Graduate level of the APST before you can graduate. If you have a teaching degree in Australia and are a registered teacher, you will have met the Graduate level of the APST.
In most states in Australia, you will be expected to move from the Graduate to Proficient level of the APST within a few years. Some employers will not allow you to move past a particular pay grade until you do this, and some registering bodies will not allow you to continue to be a registered teacher if you cannot provide evidence that you have reached the Proficient stage within a certain amount of time.
How you can become recognised as a Proficient or higher teacher depends on your state and registering body.
See more: Is it Worth Becoming a Highly Accomplished Teacher?


